The principle of operation of a car crankshaft is its structure and lubrication system.

The content of the article:
- Principle of operation
- Crankshaft device
- Crankshaft lubrication system
Each element that makes up an internal combustion engine is an integral part of the system, on which the quality of the whole mechanism depends. They perform the most important function, which is to facilitate the transformation of the reciprocating dynamics of the pistons into torque. In addition, this mechanism reacts to the variable effects of gas pressure that occur from time to time, and to the effect of inertial forces of the masses in motion.
An automobile crankshaft is a complete system, so it can be called a part. This part is made of high quality durable steel. The production method is forging. Sometimes cast iron acts as the main production material; in this case, production is carried out by casting. Diesel and turbocharged engines use the most durable and strong steel crankshafts.
The principle of operation of the crankshaft

At the moment of maximum removal of the piston, the cheeks and the crankshaft connecting rod are pulled out in one line. At this time, fuel begins to burn in the cylinders, and, accordingly, flammable gases are released, which move the piston towards the crankshaft. Together with it, the connecting rod also moves, the lower head of which rotates the crankshaft about its axis. As soon as it turns 180 °, the connecting rod journal begins to move in the opposite direction, thus the piston also moves.
It turns out the following picture: the piston is evenly moving away, then approaching the part, the extreme points of the piston are called "dead", since in these positions its speed is zero. Thus, we figured out how the crankshaft works.
Crankshaft device

The photo shows a diagram of the crankshaft
The system of the engine part under consideration includes the main and connecting rod journals, which are combined with each other by cheeks. As for the number of necks, the number of indigenous, as a rule, exceeds the connecting rod by one unit. Such shafts are called full support. The connecting rod journals are distinguished by a smaller diameter compared to the main journals. A counterweight is installed in the opposite direction to the crank pin. This element contributes to the balance of pistons and connecting rods. Its functioning is very important as it guarantees smooth operation of the entire engine.
The connecting rod pins are located between the two cheeks. Their name is knee. Elbows are set based on the number, method of operation and location of the cylinders, as well as on the dynamics of the engine. The main task of the knees is to maintain the balance of the DVZ, uniform ignition, and minimizing vibrations and bending moments. In addition, an important function of the crankpin is to support the crankpin.
In the crankshaft device system, the area where the journal of the shaft passes to the cheek has the greatest degree of congestion. In order for the stress concentration to be at a low level, this transition is installed with a fillet (radius of curvature). The fillet system contributes to the elongation of the crankshaft. Plain bearings, which are an integral part of the shaft, contribute to the rotational movements of the shaft in the bearings and connecting rods in the journals. The bearings are thin-walled bushings. They are made from high-quality steel tape, on the surface of which an anti-friction solution is applied.
To prevent rotation of the liners near the neck, a protrusion is installed that fixes their location in the support. And in order to avoid axial dynamics of the crankshaft, a sleeve bearing is used. It is installed on the root neck (extreme or inner middle).
- Learn about ways to check the crankshaft sensor
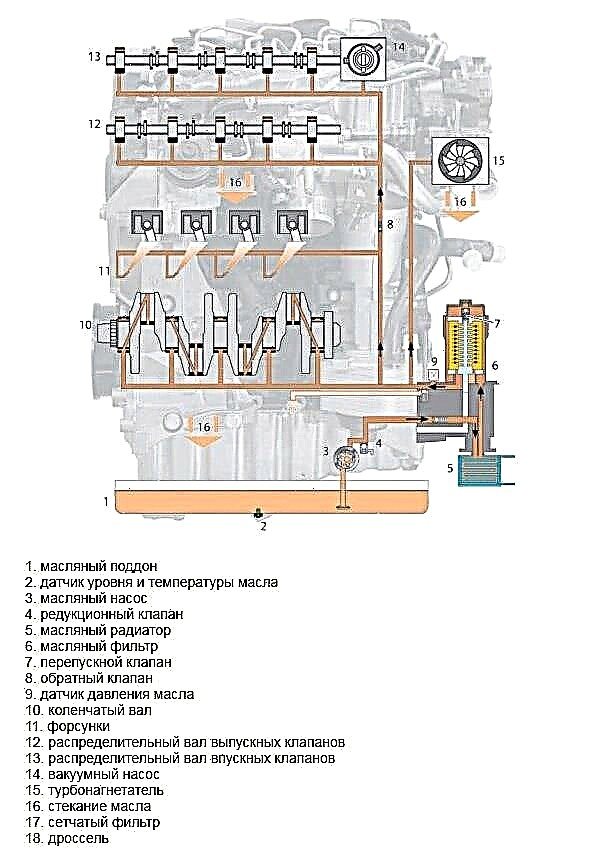
Crankshaft lubrication system
The DVZ lubrication system includes both connecting rod and main journals. They are lubricated under pressure. The common line for supplying oil to engine elements supplies it to each journal support. After this, oil is supplied to the connecting rod journals.
Power from the crankshaft is taken from its shank (reverse). At the end of the front part of the shaft, places are installed on which the shaft drive gear, pulley and torsional vibration damper are fixed. In general, they are two discs connected by a material with a high degree of elasticity (rubber, spring part, liquid silicone). These substances are able to absorb vibration of the shaft, carrying out friction inside it.

The photo shows a diagram of the crankshaft lubrication system